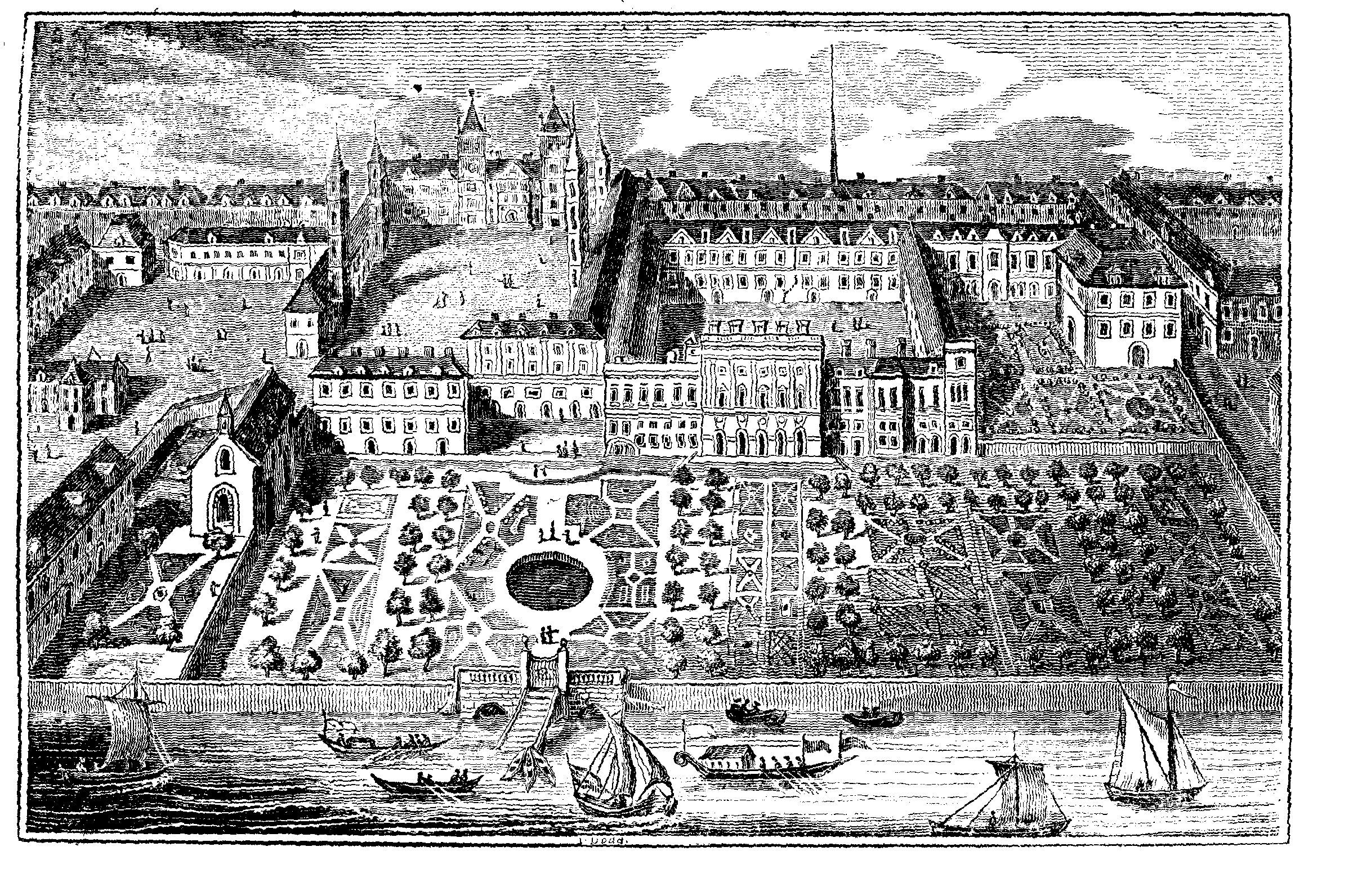
 OLD SOMERSET HOUSE.
OLD SOMERSET HOUSE.The Project Gutenberg EBook of The Mirror of Literature, Amusement, and Instruction, No. 365, by Various This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.net Title: The Mirror of Literature, Amusement, and Instruction, No. 365 Author: Various Release Date: July 10, 2004 [EBook #3246] Language: English Character set encoding: ISO-8859-1 *** START OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK MIRROR OF LITERATURE *** Produced by Jonathan Ingram and PG Distributed Proofreaders
| Vol. XIII, No. 365. | SATURDAY, APRIL 11, 1829. | [PRICE 2d. |
The Engraving on the annexed page is, perhaps, one of the greatest antiquarian treasures it has for some time been our good fortune to introduce to the readers of the MIRROR. It represents the original SOMERSET HOUSE, which derived its name from Edward Seymour, Duke of Somerset, maternal uncle to Edward VI., and Protector of the realm during most of the reign of that youthful sovereign. The time at which this nobleman commenced his magnificent palace (called Somerset House) has been generally faxed at the year 1549; but that he had a residence on this spot still earlier, is evident from two of his own letters, as well as from his "cofferer's" account, which states that from April 1, 1548, to October 7, 1551, "the entire cost of Somerset House, up to that period, amounted to 10,091l. 9s. 2d." By comparing this sum with the value of money in the present day, we may form some idea of the splendour of the Protector's palace, as well as from Stow, who, in his "Survaie," second edition, published in 1603, styles it "a large and beautiful house, but yet unfinished." The architect is supposed to have been John of Padua, who came to England in the reign of Henry VIII.—this being one of the first buildings designed from the Italian orders that was ever erected in this kingdom. Stow tells us there were several buildings pulled down to make room for this splendid structure, among which he enumerates the original parish church of St. Mary-le-Strand; Chester's or Strand Inne; a house belonging to the Bishop of Llandaff; "in the high street a fayre bridge, called Strand Bridge, and under it a lane or waye, down to the landing-place on the banke of Thames;" and the Inne or London lodging of the Bishop of Chester and the Bishop of Worcester. Seymour states, that the site of St. Mary's church became a part of the garden of Somerset House; and that when the Protector pulled down the old church, he promised to build a new one for the parishioners, but his death prevented his fulfilling that engagement. The Strand Bridge formed part of the public highway; and through it, according to Maitland, "ran a small watercourse from the fields, which, gliding along a lane below, had its influx to the Thames near Somerset Stairs."1
Besides the places above mentioned, the palace-building Protector pulled down part of the Priory church of St. John, Clerkenwell, a chapel and cloisters near St. Paul's cathedral, for the sake of the materials. He was, however, soon overtaken by justice, for in the proclamation, October 8, 1549, against the Duke of Somerset, previously to his arrest, he is charged with "enriching himselfe," and building "sumptuous and faire houses," during "all times of the wars in France and Scotland, leaving the king's poore soldiers unpaid of their wages." After the attainder and execution of the Protector, on Tower Hill, January 22, 1552-3, Somerset Place devolved to the Crown, and was conferred by the king upon his sister, the Princess Elizabeth, who resided here during her short visit to the court in the reign of Queen Mary. Elizabeth, after her succession to the throne, lent Somerset Place to Lord Hunsdon, (her chamberlain,) whose guest she occasionally became. He died here in 1596. On the death of Elizabeth, it appears to have become a jointure-house, or dotarial palace, of the queens' consort; of whom Anne of Denmark, queen of James I. kept a splendid court here. Arthur Wilson, in his "History of King James," generally calls this mansion "the queen's palace in the Strand;" but it was more commonly called Denmark House; and Strype says that by the queen "this house was much repaired and beautified, and improved by new buildings and enlargements. She also brought hither water from Hyde Park in pipes." Dr. Fuller remarks that this edifice was so tenacious of the name of the Duke of Somerset, "though he was not full five years possessor of it, that he would not change a duchy for a kingdom, when solemnly proclaimed by King James, Denmark House, from the king of Denmark lodging therein, and his sister, Queen Anne, repairing thereof."
Pennant says, "Inigo Jones2 built the back-front and water-gate about the year 1623;" but it may be questioned whether these were not the new buildings spoken of as having been previously raised by Anne of Denmark. Pennant likewise speaks of the chapel which was begun by Jones in the same year.
Denmark House was next fitted up for Henrietta Maria, queen of Charles I., and settled on her for life. By her marriage articles, extraordinary concessions were made in favour of the Catholics. The queen was not only allowed to have, herself, the free exercise of the "Roman Catholic Apostolic religion," but all her [pg 243] children were to be brought up in the same faith; she was to have a chapel in all the royal palaces; a bishop of her own faith was to be her almoner; twenty-eight priests, or ecclesiastics, were to serve in her chapel; the domestics of her household were to be French Catholics, &c. Thus, this mansion became the very focus of Catholicism, and a convent of Capuchin friars was established here by the queen. At length, in 1642, it was ordered by the Parliament that "the altar and chapel in Somerset House be forthwith burnt," and that the Capuchins be "sent into France."
In 1659, the Commons resolved that Somerset House, with all its appurtenances, should be sold for the partial discharge of the great arrears due to the army; and Ludlow states, that it was sold for 10,000l. except the chapel; but the restoration of King Charles prevented the agreement from being fulfilled.
This mansion was frequently used for the state reception of the remains of deceased persons of high rank previously to their interment. The Protector, Oliver Cromwell, was laid in state here; and Ludlow states, that the folly and profusion of this display so provoked the people, that they "threw dirt, in the night, on his escutcheon, that was placed over the great gate of Somerset House." After the restoration of Charles II. Somerset House reverted to the queen dowager, who returned to England in 1660; went back to France, but returning in 1662, she took up her residence at Somerset House; when Cowley and Waller wrote some courtly verses in honour of this edifice, the latter complimenting the queen with Somerset House rising at her command, "like the first creation."
In 1670, the remains of Monck, Duke of Albemarle, were laid here "for many weeks in royal state." For several years subsequently to this period the mansion was but little occupied; but in 1677, the Prince of Orange, afterwards William III., resided here for a short period prior to his marriage. In 1678, Somerset House became the reputed, if not the real scene of the mysterious murder of Sir Edmund Berry Godfrey, which is attributed to the Papists connected with the chapel establishment of Catherine of Braganza, queen of Charles II.; to whom this mansion was destined, contingently, as a jointure-house, and who was occasionally lodged here when Charles's gallantries had rendered it incompatible for her to be at Whitehall. On the king's decease, in 1685, she removed hither entirely, and kept her court here till 1692, when she departed for Portugal, leaving her palace to the Earl of Faversham, who continued to inhabit it till after the decease of the queen dowager in 1705.
From a description about 1720, we learn that "the stately piles of new brick houses on both sides of Somerset House, much eclipse that palace." At the entrance from the Strand, "is a spacious square court, garnished on all sides with rows of freestone buildings, and at the front is a piazza, with stone pillars, and a pavement of freestone. Besides this court there are other larger ones, which are descended towards the river by spacious stairs of freestone. The outward beauty of this court appears by a view from the water, having a good front, and a most pleasant garden, which runs to the water side. More westward is a large yard adjoining to the Savoy, made use of for a coach-house and stables; at the bottom of which are stairs, much used by watermen, this being a noted place for landing and taking water at." The water gate was ornamented with the figures of Thames and Isis, and in the centre of the water-garden was a statue. The principal garden was a kind of raised terrace, (ascended by steps from the water side) in which there was a large basin, once dignified with a fountain. The ground was laid out in parterres, near the angles of which statues were placed; one of them, a Mercury, in brass, had been appraised, in 1649, at 500l.
In the early part of the last century, Somerset House was occasionally appropriated to masquerades and other court entertainments. In the reign of George II. William, Prince of Orange, resided here a short time; and in 1764, the hereditary Prince of Brunswick became an inmate, prior to his nuptials with the Princess Augusta, sister to George III. In April, 1763, a splendid fete was given here to the Venetian ambassadors, who were entertained several days in this mansion.
In the year 1761, the second of his late majesty, Somerset House was settled on the queen consort, in the event of her surviving the king; but in April, 1775, in consequence of a royal message to Parliament, it was resolved, that "Buckingham House, now called the Queen's House," should be settled on her majesty in lieu of the former, which was to be vested in the king, his heirs and successors, "for the purpose of erecting and establishing certain public offices." An act was consequently passed in the same year, and shortly afterwards the building of the present stately pile was commenced under the superintendence of the late Sir William Chambers. Extensive, however, [pg 244] as the buildings are, the original plan has never been fully executed, and the eastern side is altogether unfinished. The splendour of the building is, however, shortly to be completed by the erection of another wing, to be appropriated as the King's College; and surveys have already been made for this purpose.
The print represents the original mansion, or, we should rather say, city of mansions, with its monastic chapel, and geometrical gardens, laid out in the trim style of our forefathers. The suite of state apartments in the principal front was very splendid, and previously to their being dismantled by Sir William Chambers, they exhibited a sorry scene of royal finery and attic taste. Mouldering walls and decayed furniture, broken casements, falling roofs, and long ranges of uninhabited and uninhabitable apartments, winding stairs, dark galleries, and long arcades—all combined to present to the mind in strong, though gloomy colours, a correct picture of the transitory nature of sublunary splendour.
In the distance of the print is the celebrated Strand maypole, although its situation there does not coincide with that marked out in more recent prints. The original of our Engraving is a scarce print, by Hollar, who died in 1677.
In the year 1650, an act was passed for the sale of the "honours, manors, and lands heretofore belonging to the late king, queen, and prince," for the payment of the army; and under that act were sold several tenements, &c. "belonging unto Somerset House." In this list were several signs, and it is remarkable, that the Red Lion, (opposite the Office of the Mirror, and at the corner of Catherine-street, in the Strand) is the only one which now remains. The Lion may still be seen on the front of the house. The Red Lion wine vaults, three doors from this corner was probably named from the above, since nearly every house formerly had its sign.
City of God—thy palaces o'erthrown—
Thy nation branded—tribes o'er earth dispersed:
Thy temple ruin'd, and thy glory fled,—
Speak of thy impious crimes, thy daring guilt,
And tell a tale whose lines are traced in blood.
No more from hence ascends
The sacrificial smoke; the priest no more
Sheds blood of lambs, to expiate thy crimes—
Crimes foul as hell—crimes which the blood of Him,
Who came from heaven to die for guilty man,
Alone could purge,—and innocence impart.
Here holy David tuned his harp to strains
Sublime as those of angels, when he sung
In dulcet melody the praise of Him
Who should redeem from guilt the sons of man,
And rescue who in Him believed from death—
That second death—of which the first is type.
Here lived—here died—whom prophets long foretold,
Whom angels worship and whom seraphs praise,
The Son of God, mysterious God-Man:
He was rejected by the Jew; and here—
To fill the awful measure of their guilt—
At noon, a deed was done, without a peer;
A deed, unequalled since the world began,
The masterpiece of sin, of crime the chief;
At which the sun grew dark, earth's pillars shook,
Chaotic gloom as erst o'erspread the land,
And nature frowned at insults paid her God—
The crucifixion of His only Son.
Here now the banner of the prophet false,
Unfolds its silken folds to taunt the Jew;
The moslem minarets lift high their heads.
And raise their summits in the placid sky—
As tho' to rouse from his deep lethargy
The hardened Jew; to wrest from Paynim hordes
The Holy City, once the abode of God.
But shall Mohammed's banner ever float
On Salem's ruins? Shaft her sacred dust
Where Christ has shed His blood, by infidels
Be ever trodden down? Shall her temple
Prostrate lie, to cause the impious mock
Of Mussulmen for ever? It may not be.
Ere many years wane in eternity,
That banner shall be plucked from its proud height—
Those tow'ring minarets shall fall to earth
And God again be worshipp'd thro' the land.
David's fair city shall be then rebuilt;
Her pristine beauty shall be far surpassed
By more than mortal splendour; her temple
Point high its turrets to the skies—and He,
The God of Hosts with glory fill the place!
S.J.
Chamberlayne in his Notitia Angliæ, says, "Before the conquest, the great council of the king, consisting only of the great men of the kingdom, was called Magnatum Conventus, or else Prælatorum Procerumque Concilium, and by the Saxons in their own tongue Micel Gemote,3 the great assembly; after the conquest about the beginning of King Edward I., some say in the time of Henry I., it was called by the French word Parlementum, from Parler, to talk together; still consisting (as divers authors affirm) only of the great men of the nation, until the reign of Henry III. when the commons [pg 245] also were called to sit in parliament; for divers authors presume to say, the first writs to be found in records, sent forth to them, bear date 49 Henry III. Yet some antiquaries are of opinion, that long before, nothing of moment wherein the lives or estates of the common people of England were concerned, ever passed without their consent."
In Edward the Third's time, an act of parliament, made in the reign of William the Conqueror, was pleaded in the case of the Abbey of St. Edmund's Bury, and judicially allowed by the court. Hence it appears that parliaments or general councils are coeval with the kingdom itself.
Sir Walter Raleigh thinks the Commons were first called on the 17th of Henry I.
Parliamentum de la Blande, was a denomination to a parliament in Edward the Second's time, whereto the barons came armed against the two Spencers, with coloured bands on their sleeves for distinction.
Parliamentum Insanum, was a parliament held at Oxford, anno 41 Henry III. so called, because the lords came with great retinues of armed men to it; and many things were violently transacted therein against the king's prerogative.
Parliamentum Indoctorum, was a parliament held at Coventry, 6th Henry VI. whereunto by special precept to the sheriffs of the several counties, no lawyer, or person skilled in the law was to be called.
Parliamentum Diabolicum, was a parliament held at Coventry, 38th Henry VI. wherein Edward, Earl of March (afterwards king) and several others were attainted. The acts passed therein were annulled in the succeeding parliament.
"In 1524, April 15, (says Stowe) a parliament was begun at the Blacke Friers, wherein was demanded a subsidy of £800,000. to be raised of goods and lands, four shillings in every pound; and in the end was granted two shillings. This parliament was adjourned to Westminster, among the blacke monks, and ended in the king's palace there the 14th of August, at nine of the clocke in the night, and was therefore called the Blacke Parliament."
Parliaments formerly sat in Westminster Hall and the Chapter house. "In 1397, (says Pennant) when in the reign of Richard II. the hall was extremely ruinous, he built a temporary room for his parliament formed with wood, covered with tiles. It was open on all sides, that the constituents might see every thing that was said and done; and to secure freedom of debate, he surrounded the house with 4,000 Cheshire archers, with bows bent, and arrows knocked ready to shoot. This fully answered the intent, for every sacrifice was made to the royal presence."
The place where the commons of Great Britain, now hold their assemblies, was built by king Stephen, and dedicated to his namesake the proto-martyr. It was beautifully rebuilt by Edward III. in 1347, and by him made a collegiate church, and a dean and twelve secular priests appointed. Soon after its surrender to Edward VI. it was applied to its present use. The revenues at that period were not less than £1,085 a year.
When the royal assent (says de Lolme) is given to a public bill, the clerk says, le Roy le veut. If the bill be a private one, he says, soit fait comme il est désiré. If the bill has subsidies for its objects, he says, le Roy remercie ses loyaux sujets, accepte leur benevolence ainsi le veut. Lastly, if the King does not think proper to assent to the bill, the clerk says, le Roy s'en avisera; which is a mild way of giving a refusal. This custom was introduced at the conquest, and has been continued, like other matters of form, which sometimes exist for ages after the real substance of things has been altered; and judge Blackstone expresses himself on this subject in the following words:—"A badge, it must be owned, (now the only one remaining) of conquest; and which one would wish to see fall into total oblivion, unless it be reserved as a solemn memento to remind us that our liberties are mortal, having once been destroyed by a foreign power." (De Lolme.) Under the walls of the legal parliament, there is held an illegal parliament, composed of livery men, who assemble in the members' servants waiting-room. Every year, a speaker or chairman is chosen, and each member addresses the other by the title his master bears. In case of disputes, &c., the speaker (who sits in an elevated chair) decides, and if there is any unparliamentary conduct, the party is fined.
This ground parliament has powers peculiar to itself, and never interferes with the upper parliament under the same roof, its powers not being so great as the "Senatus populusque Romanus." It is an annual parliament, but does not extend to universal suffrage. The members vacate their seats or stands, when discharged by their masters in the upper, or legal parliament. This parliament prints no journals, its acts not extending beyond the room, except when the Irish members turn out in palace yard. N.B. No member can be admitted till the fees [pg 246] are paid. For further information relating to this self-elected parliament, see the rules and regulations over the mantelpiece in the room.
P.T.W.
The legitimate name of Mr. Hornor's colossal edifice in the Regent's Park, we believe, was first set forth as the Gyrôrama, Girorama, Panopticon, or General View. The Catholic Church of Berlin, although diminutive in proportion to the Marylebone wonder, is, with the solitary exception of the Pantheon at Rome, the only structure, perhaps, that bears any resemblance to it in form and feature.
The porch, or, more properly speaking, the ôropylaion, or fore-temple, is about the height of our Pantheon facade in Oxford Street; and the apex of the dome may probably correspond in elevation with the roof of that building. The whole effect, however, when viewed from the great square in front of the opera house at Berlin, is extremely pleasing; and, associating itself by general outline with the ideas of the grand prototype of the eternal city, derives a degree of importance which a minuter inspection would not confer. There are numerous churches in Berlin, but three only which lay claim to particular notice, St. Nicolas, the French Church, (standing on one side of the above mentioned square) and the Catholic Church. The architecture of these is not pure in any single instance; it having been the prevailing taste of the period when they were erected to over-charge the building with ornament, and substitute one or more gorgeous embellishments as appendages to the design, for that chaste and elegant simplicity which is so essential a part of grandeur. Accordingly we find several of the largest ecclesiastical edifices, the site and contour of which would otherwise entitle them to distinction, disfigured by some overpowering frontispizio, and presenting a complication of decorative details which distort the outline, and, in spite of toilsome and finished sculpture, mar the truth and elegance of classic design.
There are seven doors surmounted by tablets of tolerably good sculpture from scriptural history, five in the front and two at the sides of the porch, the pediment of which rests on six columns of the Ionic order, and is enriched by alto relievos, illustrative of our Saviour's ministry, as also by marble statues representing the Virtues, &c. The entablature bears an inscription relative to the occasion and date of this building being erected in the last century. The interior is plain, and more conspicuous for an accumulation of dirt and dust (a very common characteristic of Berlin) than of ornament; the four-and-twenty Corinthian columns, however, which contribute their support to the dome are imposing in their appearance. The high altar and sacristy are constructed in a recess formed by the annexation of a small chancel to the rotunda. This church, built of freestone, stands in an angle of the Place des Gens d' Armes, immediately behind the great Salle des Spectacles (schauspielhaus) or theatre, in one of the finest squares of Berlin. With the exception of a few small chapels, it is the only Catholic place of worship in that city, the religion of Prussia being chiefly Lutheran.
J.R.
An interesting discovery of paintings by Hogarth, viz. "The Modern Midnight Conversation," and the "Hudson's Bay Company's Porters going to Dinner," was made about three years' ago, upon the demolition of the old Elephant public-house, Fenchurch-street.4 The pictures were the undoubted productions of Hogarth, something more than one hundred years since, at which time he lodged there. The house was known as the Elephant and Castle, where it had been customary for the parochial authorities to have an entertainment, the celebration of which, from some cause, was unexpectedly removed to Harry the Eighth's head, opposite, and still in the same line of business. This removal being mentioned to our artist on his return home at night, irritated him not a little, at what he considered the neglect with which he had been treated in not being invited as formerly. He therefore went over to the King's Head, where some discussion took place, which it is supposed was not very amicable, as he left them (as the clock indicates, at past four in the morning,) threatening to stick them all up on the walls of the tap-room in the Elephant and Castle, which, as an eminent modern artist said, most emphatically, upon his first seeing the picture after it had been removed and placed on canvass,—Hogarth had done Con Amore.
The proposition being made to the host, he agreed to wipe out Hogarth's score upon his completing the picture, which attracted much company; so that, although the house lost the dinner party, it gained [pg 247] by persons coming to see the parochial authorities stuck up on the walls. Some time after, the score again raised its head, when mine host, for the purpose of clearing it off, and to make the tap-room more uniform, proposed to Hogarth the subject of the Hudson's Bay Company's porters going to dinner; they at that time, as they still do, frequenting the house. This picture represents Fenchurch-street as it appeared more than a century ago, with the old Magpie and Punch Bowl public-house in the distance, which house has not long since been taken down. The Elephant public-house was taken down and rebuilt in 1826, and is now occupied by Mrs. Eaton, in whose family the business has been for more than a hundred years, and from whom these particulars have been obtained. The first named picture is considered to be the original from which Hogarth afterwards painted the one known as the "Modern Midnight Conversation," in which there are one or two figures less than in the original. Orator Henley and the other principal characters, occupy the same situation in both performances.
Mr. Soane, the architect, upon hearing of the present condition of the pictures, said, that he in early life, while at Rome, knew that various attempts had been made for the purpose of removing oil paintings from walls, but without success, and expressed himself highly gratified at the result of the exertions of the persons who bought and removed them at no small risk and expense, viz. Mr. Lyon, 5, Apollo-buildings, East-street, Walworth, and Mr. H.E. Hall, a Leicestershire gentleman of great ingenuity; who have placed them for sale in the gallery of Mr. Penny, in Pall Mall.
A CONSTANT READER.
Ambition is a vulture vile,
That feedeth on the heart of pride,
And finds no rest, when all is tried,
For worlds cannot confine the one
Th' other lists and bounds hath none
And both subvert the mind, the state,
Procure destruction, envy, hate.
S. DANIELL.
In this great temple richly beautified,
Pav'd all with stars, dispers'd on Sapphire flower,
The clerk is a pure angel sanctified,
The Judge our High Messiah full of power,
The Apostles his assistants every hour,
The jury saints, the verdict innocent,
The sentence, come ye blessed to my tent.
The spear that pierc'd his side, the writing pen,
Christ's blood the ink, red ink for prince's name,
The vailes great breach, the miracles for men,
The sight is show of them that long dead came
From their old graves, restored to living fame.
And that last, signet passing all the rest,
Our souls discharg'd by consummatum est.
Here endless joy is their perpetual cheer
Their exercise, sweet songs of many parts.
Angels their choir, whose symphony to hear
Is able to provoke conceiving hearts
To misconceive of all enticing art
The ditty praise, the subject is the Lord,
That times their gladsome spirit to this accord.
TH. STOKER.
Is't not God's deed whatever thing is done
In heaven and earth? Did not he all create
To die again? all ends that were begun;
Their times in his eternal books of fate
Are written sure, and have their certain date,
Who then can strive with strong necessity,
That holds the world in his still changing state?
Or shun the death ordain'd by destiny,
When hour of death is come, let none ask whence or why.
SPENSER.
Fraud showed in comely clothes a lovely look,
An humble cast of eye, a sober pace;
And so sweet speech, a man might her have took
For him that said "Hail Mary full of grace;"
But all the rest deformedly did look.
As full of filthiness and foul disgrace;
Hid under long, large garments that she wore,
Under the which, a poisoned knife she bore.
SIR J. HARRINGTON.
What one art thou thus in torn weeds yclad?
Virtue, in price, whom ancient sages had—
Why poorly clad? for fading goods past care—
Why double fac'd? I mark each fortunes rare;
This bridle, what? mind's rages to restrain—
Why bear you tools? I love to take great pain—
Why wings? I teach above the stars to fly—
Why tread your death? I only cannot die.
WYAT.
Of all God's works which doth this world adorn,
There is none more fair and excellent
Than is man's body, both for power and form,
Whilst it is kept in sober government,
But none than it more foul and indecent,
Distempered through misrules and passions base,
It grows a monster and incontinent,
Doth lose his dignity and native grace.
SPENSER.
Never have unjust pleasures been complete
In joys entire: but still fear kept the door.
And held back something from that hell of sweet,
To intersour unsure delights the more
For never did all circumstances meet
With those desires that were conceiv'd before,
Something must still be left to cheer our sin,
And give a touch of what should not have been.
DANIELL.
He that compar'd man's body to a host
Said that the hands were scouts discovering harms,
The feet were horsemen thundering on the coast,
The breast and stomach foemen, huge in swarms,
But for the head in sovereignty did boast,
It captain was, director of alarms,
Whose rashness if it hazarded any ill,
Not he alone, but all the host did spill.
MARKHAM.
Sweet solitary life thou true repose,
Wherein the wise contemplate heaven aright,
In thee no dread of war or worldly foes,
In thee no pomp seduceth mortal sight.
In thee no wanton cares to win with words,
Nor lurking toys which silly life affords.
D. LODGE.
What so strong
But wanting rest, will also want of might?
The sun that measures heaven all day long,
At night doth bathe his steeds th' ocean waves among.
SPENSER.
A stronger hand restrains our wilful powers.
A will must rule above the will of ours,
Not following what our vain desires do woo,
For virtue's sake, but what we only do.
DRAYTON.
He only lives most happily
That's free and far from majesty—
Can live content although unknown—
He fearing none, none fearing him—
Meddling with nothing but his own—
While gazing eyes at crowns grow dim.
KYD.
Content feeds not on glory nor on pelf,
Content can be contented with herself.
BASTARD.
We trust we have consulted the profitable amusement of the reader, in condensing the following very interesting facts from the Second Part of Sir Richard Phillips's Personal Tour through the United Kingdom; since, as the author observes, "if the less active districts of the home counties afforded materials worthy of attention, the more industrious counties of DERBY and NOTTINGHAM are not less likely to add interest to the pen of an observer. In truth, the public spirit which more actively prevails in these counties, added facilities to inquiry; while the objects described have so many peculiar features, that a full and popular account of them must be as new to the nation at large as they were to the writer."
After passing a pleasant night and morning near Swarkeston, I drove eight miles, through a country of limestone and gypsum; of activity and great beauty, to the centrical and classical town of Derby. In position, it is the centre of the kingdom, not only geographically, but commercially.—It is forty miles within the manufacturing circle, passing southward, and from forty to sixty miles around, there is the most industrious space on the globe; while no one can think about Derby, without associating the names of Darwin, in poetry and philosophy; of Wright, in painting; and of the Strutts, as the patrons of all the useful and elegant arts. I entered Derby, therefore, with agreeable associations, and they have since been realized.
Taken altogether, Derby is a medium town, between a manufacturing and a genteel one. This, in variety, is an advantage, for while the manufacturers are improved in manners, gentility is more substantial. It is neither wholly vulgar, like some places, nor poor and proud, like others. For its size, it is a rich town. I was told, there are five or six persons in it worth £100,000. and upwards, each, and as many more worth 30 or £40,000. In most country towns there are fewer such, but Derby is fortunate in its geographical and natural position, and in the prudence of its genius and industry.
I proceeded to Belper, eight miles, to view the superb establishment of the Messrs. Strutt, as cotton spinners. The excellent road, which continues to Matlock, and the north, lay through the most delightfully variegated country which I had seen since I left Hertfordshire. The village of Duffield, in a valley of the Derwent, with houses on the steep eastern bank, and woods to the top, is one of the prettiest to be seen. On crossing the river, I beheld long lines of cottages, built for the residence of the families employed in Messrs. Strutts' smaller factory at Melford. Passing this, the extensive but straggling and picturesque town of Belper, covered the eastern hill. What remains of the old town, is not a tithe of the present one, and the whole is now supported by Messrs. Strutts' gigantic mills.
I approached these with mingled pleasure and astonishment. A manufactory, in such hands, presented none of the usual drawbacks on one's feelings. They never discharge their workmen; and good conduct is a life interest in comfort! The picturesque beauty of the situation, the height and extent of the buildings, and the increase of the busy throng, as I entered the yard, was exhilarating. The effect grew as I approached, for the distance of two or three hundred yards, the noise, produced by the united rattling of thousands of small wheels, was like the sound of a hail storm on a large sky-light, or the fall of an immense sheet of water.
[pg 249]There are five oblong factories and two circular ones. The five are six stories high, with ten or twelve windows on each story, so that in the five there are, at least, as many regular windows as days in the year. The circular buildings have forty or fifty more.
In this establishment, and at Melford, Messrs. Strutt employ, at present, about 1,300 hands of both sexes and different ages, and spin about 18 tons, or 40,000 lbs. of cotton per week. The average fineness may be taken at 20 hanks to the pound, and hence, as each hank is 840 yards, or nearly half a mile, every pound is nearly ten miles, and the whole, about 400,000 miles are produced in about sixty-six working hours. In round numbers, this is 6,000 miles per hour, or 100 miles a minute. What an astonishing effect of the combination of mechanism! What an inconceivable miracle, if it might not be witnessed by their favour at any time!
Nor should it be forgotten, that every fibre passes through no less than ten sets of machinery, hence, the united spindles and threads travel through 1,000 miles a minute. The noise of their united frictions and collisions, and the united hum of thousands of little spindles, each revolving 4,000 times a minute, may, therefore, be accounted for, but can never be conceived, unless heard in the midst of them.
It would be tedious to dwell on the well-known process of cotton spinning; but as this manufactory produces the cleanest and most perfect yarn made in England, of its numbers from 6 to 100, it may be worth while to state, that this perfection appears to arise, from the systematic perfection of all the machines, and from the astonishing cleanness of every part of this great factory. The wheels are as bright as the grate of a good housewife's drawing-room; every action is complete in its way, and though cotton is a dusty article, yet I no where saw either dirt or dust. At the same time, order prevails throughout, for as the main shaft gives no respite to the carding, roving, and spinning machines, so every attendant diligently and silently watches the lines of bobbins which are performing their miraculous evolutions, while the other apparatus are correcting and regulating the stages and steps of the production.
The whole is turned by eight or nine water wheels, of about twenty-four feet diameter, and twenty feet in length. The fall is about twenty feet, and the admirable contrivances of revolving balls (adopted in the steam-engine) are affixed, to render the power uniform, by varying the depth of the falling stream. In truth, it is one of the features of the entire establishment, that all, that can be performed by machinery, is so performed, and that the machinery is the very best for its purpose, and in many instances which I witnessed, as true, as decided in its action.
After the thread is wound into hanks, it is bleached at a distinct manufactory for that purpose; but as bleaching is a mere chemical operation, and the means are either known and not curious, or secret, and not proper to inquire about, I did not visit this branch of the establishment.
The first of the works on this spot, was built by Mr. Jedediah Strutt, father of the brothers, William, George, and Joseph, about fifty years since. Arkwright invented the spinning machines, while a barber's apprentice. He was joined by one Need, and they expended £14,000. with uncertain success. Wright, the banker, of Nottingham, hesitated to make further advances, and, at this juncture, they were joined by Mr. Jedediah Strutt, a careful man, with the necessary credit or capital, and the result was, the realization of princely fortunes, and the enriching even the nation itself. On the expiration of their partnership, Arkwright went on by himself at Cromford, and the Strutts for themselves at Belper. A spirit of detraction would make it appear that Arkwright stole the invention of another, but Mr. William Strutt, who knew him well, and is a competent judge on such subjects, assured me that Arkwright was a man of very superior talents as a mechanic, and quite equal to such an invention. I saw two portraits of him in Mr. Strutt's house, and no higher proof could be given of his personal respect for Arkwright, while he never failed to speak of him with enthusiasm, as a man of original talents.
Silk throwing is a considerable trade in Derby. Sir Thomas Lombe's famous machinery has not, however, been used for some years, but improved machinery, which performs twice the work, in less room, is now adopted. The chief throwsters are Messrs. Bridget, Taylor, Adcock, Butterworth, Moore and Gibson, Devenport and Forster. The silks, as imported, chiefly from Bengal and China, are in what are called books of 10 lb. of which ten form a bale, and the business of the throwster is to wind it, from the plats or skeins upon bobbins; and from these, it is twisted into two, three, or [pg 250] more threads. The price for throwing is from 1s. 9d. to 2s. for Bengals, and from 2s. 9d. to 3s. per lb. for China. About 1,500 lbs. a week are thrown, employing from 1,000 to 1,200 men, women, and children. The price used to be 4s. a lb. but a fall has taken place, within the last fifteen years, in this article of labour, as well as in every other.
I heard much from all the manufacturers of Derby, of the mechanical ingenuity of Mr. James Fox, of Chester Road, on the banks of the Derwent. I paid him a visit, and beheld his powerful iron lathes, twenty-four feet long, used by machine makers for planing iron. Here I saw iron cut in groves or squared with great simplicity, by duly adjusting the velocity so as to generate no heat, for a velocity, which generates heat, destroys the tool. These lathes, Mr. Fox makes for machinists in all parts of the kingdom, and gets from £200. to £700. for them. The castings are made at Morley Park; and I was sorry to learn that they are now delivered at £7. a ton instead of £30. the usual and legitimate price. In truth, the depression of the iron trade is as great or greater than that of the other staples of the kingdom.
The number of cotton frames employed by the above, is from 3,000 to 4,000 dispersed over the town and country; and the number of silk frames is about 1,000. The average earnings of the cotton hands are from 7s. to 10s. per week, but many frames are worked by young persons both male and female. The silk hands earn about 12s. or 15s.
A manufactory, at once local and elegant, exists at Derby, which excites the attention and loosens the purse-strings of most strangers. It is the spar-manufactory of Mr. Hall, and in it, he converts the petrified sports of nature, in the Derbyshire hills, into the luxuries of civil life. Those in London, who desire to see the products of these works, may behold them at Mawe's, in the Strand; but all, who visit Derby, will not fail to call upon Mr. Hall, who is as courteous as he is ingenious. Amythistine and other spars, white and variegated marble, alabaster, &c. are here formed in a series of workshops, aided by a steam engine, into vases, columns, obelisks, &c. &c. Tasteful statuaries are also employed, in converting the same materials into dogs, horses, sheep, cows, &c. for chimney ornaments; and Mr. Hall has likewise imitated the best vases, and some of the structures of Egypt, with exact transcripts of their inscriptions. In these works, in polishing, sawing, fashioning, &c. he employs numerous hands; and persons, whom he may indulge, with a view of the details, will be instructed and gratified.
Cromford is an immense establishment; but being inferior in magnitude to Belper, and of the same description, I forbear to enlarge upon it. Here the late Sir Richard Arkwright established the first cotton-spinning mill, and from the poverty of a barber's apprentice, became one of the wealthiest merchants in the united kingdom. The concern is now carried on by his son, and I found that his work-people were in the same state of comfort, as those of the Messrs. Strutt.
The present Mr. Arkwright, son of Sir Richard, is between seventy and eighty, and by the power of unparalleled capital and habits of frugality, he is considered the most wealthy person in Europe. I heard his accumulations estimated at six, eight, and even ten millions; and he spends but 2 or £3,000. per annum. He has eight children, and provides liberally for them, and I heard some anecdotes of his munificence to the deserving, but do not consider myself at liberty to repeat them. His habits lead him to continue in business, though the profits are now trifling. Those of his father and his own, formerly, were 2 or 300 per cent, but competition has now rendered them nearly nominal.
At Ashford, my sympathy was strongly excited by the procession of a village funeral, in which the affections of the people seemed concerned. I found on inquiry, that the corpse was the wife of the schoolmaster, who, in her prime, and in the enjoyment of general esteem, had been cut off in childbirth. The clergyman headed the procession. The coffin was borne by eight females, in white hoods and scarfs, and was followed by the unhappy husband, who conferred great effect, in the display of his grief, by carrying in his arms two young children, the offspring of the deceased. A long train of mourners followed, and I question whether more tears are shed, or more sensibility exhausted, at funerals accompanied with heraldic pomp, than in this simple display of natural affection. I drew up my horse as the procession passed, and the affair threw a gloom over my spirits, in which it seemed as though the village at large partook. The funeral group, with the father and his children, and the sorrowful countenances of the [pg 251] well disposed population, would have made a beautiful subject for a sentimental painter.
The present population of these triangular midland towns, are, Leicester, 35,000; Derby, 22,000; and Nottingham, 50,000, in round numbers, and this adds sufficiently to the last population returns. The proportional comfort in each, respectively is 8, 10, and 5—the good taste, 6, 7, and 4—the manners, 5, 8, and 4—the wealth, 4, 6, and 5—the style of the towns, 4, 8, and 2—the industry, 6, 5, and 8—the political spirit, 4, 3, and 10—the religious fervour, 5, 4, and 10—the returns in trade, 5, 6, and 10—the superfices, 6, 4, and 6—the poverty, 6, 2, and 10—the literature, 4, 5, and 4—the musical taste, 5, 3, and 2. Of course, in assigning these numbers, I may err in a fraction; but I make my determinations on my own observations and personal impressions, after diligently observing each place.
Mr. Henry Augustus Constantine Stubbs (or as he distinguished himself on his new visiting cards, H.A.C. Stubbs) had taken up his abode in one of the demi-fashionable squares, among judges, physicians, barristers, and merchants, at the north side of the metropolis. Being the only lawfully begotten issue of his father, when the frail Angelina made it impossible he should have any brothers and sisters, he succeeded, by will, to three-fourths of the late Mr. Jonathan Stubbs's property, and, by oxalic acid, to the remaining fourth;5 the affair being too sudden to permit of any further testamentary dispositions, or of any of those benevolent codicils, which sometimes have the effect of tapering down primary bequests, like Prior's Emma, "fine by degrees and beautifully less." Upon a fair computation, after a few trifling legacies were paid, and all debts satisfied, young Mr. Stubbs might calculate his inheritance, in India stock, Bank stock, houses, canal shares, and exchequer bills, at nearly eighty thousand pounds.
His education had not been neglected; that is to say, his father sent him, at nine years old, to one of those suburban seminaries for "young gentlemen," usually kept by elderly gentlemen, who know what it is to have been deprived of similar advantages in their own youth. They feel, therefore, a laudable gratification in enabling the rising generation to pluck some of that fruit from the tree of knowledge which they themselves never tasted at all. Here he remained till he was nearly seventeen; and here he acquired a little French, a little Greek, a little Latin, a little mathematics, a little logic, and a little geography, "with the use of the globes." In short, he brought away with him a little learning, for the obtaining of which his father had not paid a little money. He subsequently enlarged his Lilliputian stock of ideas, by assiduously prosecuting his studies at home, three days a-week, and three hours a-day, when he was attended by masters in elocution, Italian, boxing, fencing, and the other sciences. This eager cultivation of his mind he pursued till he was two and twenty, and then took his station in about the third degree of fashionable society, as a scholar and a man of taste. His father had determined he should be a gentleman, and therefore very properly guarded against the "anachronism," as he used to call it, of giving him a profession. It is believed, (at least it has been inculcated,) that there exists, in every human mind, a master, or ruling passion—a predominating inclination towards some particular object or pursuit. Mr. Henry Augustus Constantine Stubbs, was in this respect, as well as in many others, like the rest of his species. He had his ruling passion, and, but that his father had made him a GENTLEMAN, he was sure nature had intended him for the Roscius of his age. From his earliest childhood, when he used to recite, during the Christmas holidays, "Pity the sorrows of a poor old man," and astonish his father's porter (who had a turn that way himself) with his knowing, all by heart, "My name is Norval, on the Grampian hills,"—to his more matured efforts of, "Most potent, grave, and reverend signiors," or, "My liege, I did deny no prisoners,"—the idea of being an actor had constantly fascinated his imagination.
It was a natural consequence of this [pg 252] theatrical ardour, that Mr. Stubbs eagerly cultivated the acquaintance of tragedians, comedians, managers, and dramatic writers. It was his supreme delight to have them at his table; and as he kept a good table, gave good wines, and excelled in his cuisine, it was a delight he could command whenever he chose. He had the entré, also, of the green-room at both theatres, and acquired an intimate knowledge of all the feuds, rivalries, managerial oppressions, intrigues, burlesque dignity, and solemn plausibilities, of that mimic world. Living thus in an atmosphere electrical, as it were, with excitement, it is no wonder that, by degrees, he became less and less sensitive with regard to that ambiguous difficulty which had hitherto impeded the gratification nearest his heart.
It happened one morning while Mr. Stubbs was sipping his chocolate and reading, in the Morning Post, a criticism upon a new tragedy which had been most righteously damned the night before, that his intimate friend Mr. Peaess, the manager of —— theatre dropped in. After the usual salutations were exchanged, and Mr. Peaess had remarked that it was a fine morning, and Mr. Stubbs had added that it was a windy one, Mr. Stubbs fell into a brown study. His mind laboured with a gigantic purpose. It was a moment on which hung indescribable consequences.—Shall I? Will he? Yes!—yes!—And he did! He imparted to his friend, the manager, his resolution to make his FIRST APPEARANCE. He fixed upon Hamlet, chiefly because the character was so admirably diversified by Shakspeare, that it presented opportunities for the display of an equal diversity of talent in its representative.
He made no secret of his intention among his friends, and one, in particular, was privy to his whole course of preparation. This was Mr. McCrab, a pungent little personage, whose occasional petulance and acrimony, however they might rankle and fester in more sensitive natures, were never known to curdle the bland consciousness of self-esteem which dwelt, like a perpetual spring, upon the mind of Mr. Stubbs. Mr. McCrab was himself an amateur actor; he had also written a tolerably successful comedy, as well as an unsuccessful tragedy; and he was, besides, a formidable critic, whose scalping strictures, in a weekly journal, were the terror of all authors and actors who were either unable or unwilling to dispense turtle and champagne.
Mr. Stubbs, it should be mentioned, considered himself a profound reader of Shakspeare, and believed he had discovered many hitherto concealed beauties in the wonderful productions of that writer. He prided himself, too, upon the critical acumen and philosophical penetration with which he had elicited various qualities intended by the poet to belong to his characters; and he had often said if he had been an actor he should have established quite a new method of playing several of them. He was now about to become an actor, and he resolved, in his very first essay, to introduce one of his novelties, or new readings. What this was, will be best explained in the following conversation, which took place between himself and Mr. McCrab upon the subject.
"Depend upon it, my dear McCrab," said Stubbs, taking down a volume of Shakspeare from his shelves, "depend upon it, I am borne out in my opinion, novel as it is, by the text of the immortal author himself; and I shall stuff the character when I play it. I maintain Hamlet ought to be"——"A Falstaff in little, I suppose," interrupted McCrab. "No," rejoined Stubbs, "he should not be exactly corpulent—but rather embonpoint, as the saying is—sleek—plumpish—in good condition as it were."
"You talk of the text of Shakspeare as your authority," replied McCrab,—"I will appeal to the text too—and I will take the description of Hamlet by Ophelia, after her interview with him. What is her language?
'Oh what a noble mind is here o'erthrown!
The expectancy and rose of the fair state:
The glass of fashion and the mould of form,
The observed of all observers.'
This eulogium paints in distinct colours what should be the personation of Hamlet on the stage. It demands, not a little fellow, five feet five, by three feet four, as you will be, if you stuff the character as you call it, but rather what Hamlet himself describes his father to have been,
'A combination, and a form indeed.
Where every god did seem to set his seal,
To give the world assurance of a man.'"
"Never mind my height," said Stubbs, elevating his head, and raising his chin an inch or two out of his neckcloth.—"Garrick, you know, was none so tall; and yet I fancy he was considered a tolerably good actor in his day. But you remember the lines of Charles Churchill,
'There are, who think the stature all in all,
Nor like a hero if he is not tall.
The feeling sense all other wants supplies—
I rate no actor's merit from his size.
Superior height requires superior grace,
And what's a giant with a vacant face?'"
"Very true," answered McCrab, "and, [pg 253] to follow up your theory, were I asked, what is an actor? I should answer,
''Tis he who gives my breast a thousand pains:
Can make me feel each passion that he feigns;
Enrage, compose with more than magic art,—
With pity and with horror tear my heart.'
But, come; let me hear your reasons for believing that Hamlet ought to be a portly gentleman. I see you are ready with them."
"I am," said Stubbs, "and I'll bet the receipts of the house, on my first appearance, against those of your next comedy, that I convince you I am right before I have done. Now, mark,—or, as Horatio says,
'Season your admiration for awhile,
With an attent ear, till I may deliver,
Upon the witness of these same pages,
This marvel to you.'
Ha! ha! that is apt," continued Mr. Stubbs, with a simper.
"For God's love, let me hear," added McCrab—"I hope that's apt too."
"If," said Mr. Stubbs, looking exceedingly grave, "if, I say, we take the first soliloquy of Hamlet—almost the first words he utters—we shall find a striking allusion to his habit of body; and not only shall we be struck by the allusion, but, I contend, the whole force and meaning of the passage are lost, unless the speaker can lay his hands upon a goodly paunch, as he exclaims,
'Oh! that this too too solid flesh would melt.
Thaw, and resolve itself into a dew.'
We are not to suppose Hamlet speaks metaphorically, but physically; and his corporeal appearance should be an illustration of his words. He is already weary of the world—he wishes to die—but 'the Everlasting has fixed his canon against self-slaughter,' and, therefore, he prays for natural dissolution, by any wasting disease, which may 'thaw' and dissolve his 'too too solid flesh.' This, perhaps, you will consider merely conjectural criticism: plausible, but not demonstrative. I own it has a higher character in my eyes; and, unless I am greatly mistaken, even the ghost of his own father glances at his adipose tendency, when he says,
'I find thee apt
But duller shouldst thou be than the fat weed
That roots itself in ease on Lethe's wharf,
Wouldst thou not stir in this.'
That is, according to my reading, 'fat as thou art, thou wouldst be duller than the fat weed of Lethe if you did not bestir yourself in this business.' Observe, too, with what propriety Shakspeare has here employed the word 'stir,' it being a well-known fact that corpulent persons have a strong disinclination to locomotion. And Hamlet himself, (in his interview with Rosencrantz and Guildenstern,) makes a pointed allusion to the indolence and lethargy which so commonly accompany obesity. 'I have of late,' he says, 'but wherefore I know not, lost all my mirth, foregone all custom of exercises, and, indeed, it goes so heavily with my disposition,' &c. &c. Now what is this, I would fain know, if it be not the natural complaint of a man suffering under the oppression of too much flesh? or, as he afterwards expresses it, with another allusion to his fatness, 'to grunt and sweat, under a weary life?' You have quoted the language of Ophelia in support of the common notions with regard to the personation of this character; but you forget the remarkable expression she uses when describing to her father the unexpected visit of 'Lord Hamlet,' while she was 'sewing in her closet:
'At last, a little shaking of mine arm,
And thrice his head thus waving up and down,
He raised a sigh so piteous and profound,
As it did seem to shatter all his bulk,
And end his being.'
What say you to this?—His bulk! The sigh was so profound, that it seemed to shatter even his bulk! I fancy I might rest my case here, and win my wager, eh? But I am too skilful a general to throw away my strength at the beginning of a battle. If I have not already beaten you from your last strong hold—from your last defence—I have a corps de reserve, which will at once decide the victory. You remember the concluding scene, I suppose—the fencing bout between Hamlet and Laertes? What do you think of the following little bit of dialogue?
'Laertes.—A touch—a touch,—I do confess.
King.—Our son shall win.
Queen.—He's fat and scant of breath. Here,
Hamlet, take my napkin—rub thy brows
——Come, let me wipe thy face!'
Do you not imagine you see the pursy Prince, purring and blowing and sweating with the exertion he had made, and 'larding the lean earth,' like another Falstaff almost? Nay, the very words, 'Come let me wipe thy face,' are addressed by Doll Tearsheet to Falstaff, when he was heated by his pursuit of Pistol:—'Alas, poor ape, how thou sweatest! Come, let me wipe thy face.' Hem!" (quoth Mr. Henry Augustus Constantine Stubbs) "I have done—and pause for a reply."
"You'll be horribly laughed at," said McCrab, "if you do make Hamlet a fat little fellow."
"Shall I?" exclaimed Stubbs, with a contented chuckle, and rubbing his hands "shall I be horribly laughed at?"
"Ay," replied McCrab, "and gloriously gibbetted the next day, in all the [pg 254] papers, for your Sancho Panza exhibition."
"Pooh!" ejaculated Stubbs, "pooh! pooh! what care I for the rascally papers? Don't I know what sort of critics they are who guide the public taste, and fulminate their mighty WE in the columns of a newspaper."
(To be concluded in our next.)
Hermes, god of cheats and chatter,
Wave thy smooth caduceus here—
Now that, pulpit-propp'd, I flatter;
Hermes, god of cheats and chatter,
Smile, oh smile on Mr. Smatter,
Aid an humble Auctioneer!
Wave thy smooth caduceus here,
O'er an humble Auctioneer!
With its virtues tip my hammer,
Model my Grammar,
Nor let me stammer.
First, here's Sackbut's Song of Slaughter;
Verse and prose, the Laureat Otter,
Floats along, diluting song
In milk and water.
Next (who'll buy?) here's Love in Little,
Smooth as glass and eke as brittle;
Here are posies, lilies, roses,
Cupid's slumbers—out in numbers,
Pouting, fretting, fly-not-yetting,
Rosa's lip and Rosa's sign—
For one pound six—who'll buy, who'll buy?
Here's Doctor Aikin, Sims on Baking,
Booth in Cato quoting Plato,
Jacob Tonson, Doctor Johnson,
Russia binding, touch and try—
Nothing bid—who'll buy, who'll buy?
Here's Mr. Hayley, Doctor Paley,
Arthur Murphy, Tommy Durfey,
Mrs. Trimmer's little Primer,
Buckram binding, touch and try—
Nothing bid—who'll buy, who'll buy?
Here's Colley Cibber, Bruce the fibber,
Plays of Cherry, ditto Merry,
Tickle, Mickle,
When I bow and when I wriggle,
With a simper and a giggle,
Ears regaling, bidders nailing,
Ladies utter in a flutter—
"Mister Smatter, how you chatter,
Dear, how clever! well, I never
Heard so eloquent a man!"
Tropes purloining, graces coining,
Glibly I, without repentance,
Clip each sentence.
But, to give each lot its station,
Ere from pulpit I dismount
God of recapitulation,
Hermes, aid me while I count—
Aikin, Baking, Cato, Plato,
Cibber, Fibber—Cherry, Merry,
Hayley, Paley—Secker, Decker,
Tickle, Mickle—Tonson, Johnson,
Literary Caliban.
Forty-seven! Oh, far too thrifty—
Thank'ee, Ma'am—two places—fifty!
Must it go? oh, surely no!
Only eye me, then deny me.
When I bow and when I wriggle,
With a simper and a giggle,
Ears regaling, bidders nailing,
Ladies utter in a flutter—
"Mister Smatter, how you chatter—
Dear, how clever! well, I never
Heard so eloquent a man!"
Tongue of Mentor, lungs of Stentor,
Hermes, thou hast made mine own.
Cox and Robins own, with sobbings,
I'm the winner; Dyke and Skinner
Never caught so glib a tone.
Dull and misty, Squibb and Christie,
When I mount look pale and wan—
Going, going, going—gone!
New Monthly Magazine.
metres.
The highest Pyramid in Egypt- - - - - - - - - - - -146
The Cathedral at Anvers - - - - - - - - - - - - - 144
The Cathedral at Strasburg - - - - - - - - - - - - 142
The Steeple of St. Stephen, at Vienna, (Austria) - 138
The Steeple of St. Martin, at Landshut - - - - - - 137
St. Peter's, at Rome - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -132
The Steeple of St. Michael, at Hamboro' - - - - - 130.5
The Steeple of St. Peter, at Hamboro' - - - - - - 119
St. Paul's Cathedral, at London - - - - - - - - - 109.7
The Cathedral of Ulm - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -109.4
The Cathedral of Milan - - - - - - - - - - - - - 109
The Tower of the Asinelli, at Bologna - - - - - - 107
The Dome of the Invalids, at Paris - - - - - - - - 105
The Cathedral of Magdebourg - - - - - - - - - - - -101.6
The Cupola of the Pantheon, at Paris - - - - - - - 79
The Balustrade of Notre Dame, at Paris - - - - - - 66
The metre is 39.37 inches.—From the French.
In consequence of the frequent occurrence of fires in theatres, particular precautions have been taken with the theatre of the Port St. Martin, at Paris. A thick wall of hewn stone separates the audience part from the scenic part of the house; all the doors in it are of iron, and may be shut instantly, in case of fire; finally, the insulation of the spectators from the stage is made perfect by means of a screen of plates of iron, which falls down before the stage. This screen, which weighs between 1,200 and 1,300 pounds, is easily worked by two men, and slides up and down upon guides, so as readily to take its place. Besides these precautions, reservoirs of water are established in the roof, which may be connected, when necessary, with vessels of compressed air, and made to throw a powerful jet over a very large part of the building.—French Paper.
A tanner, named Rapedius, of Bern Castel, on the Moselle, has discovered a [pg 255] new species of tan proper for dressing leather. It is the plant known by the name of Bilberry or Whortleberry, (Vaccinium Myrtilus or Myrtillis,) which should be gathered in spring, because at this season it dries more readily, and is more easily ground. Three pounds and a half of this tan suffice for dressing a pound of leather, while six pounds are required from the oak to produce the same effect. By this new process, tanners can gain four months out of the time required for preparing strong leather. A commission having been appointed at Treves to examine the leather so prepared, reported, that they had never seen any as good, and that every pair of shoes made therefrom lasts two months more than what are manufactured from common leather; that the skin of the neck, which it is difficult to work, becomes strong and elastic like that of the other parts. The shrub should not be pulled up, but cut with a bill, to obtain the reproduction of the plant the following year. When cut, damp does not deteriorate it, which is not the case with oak bark, which loses ten per cent. of its value by being wetted.—From the French.
It would be very interesting to know whether the gossamer threads thrown out by these insects are in an excited state of electricity: their divergent state would seem to imply they were; for there seems to be no other natural cause which could prevent them from coming together, especially before the insect had left its resting-place. If electric, then neighbouring bodies, as the hand or branches of a tree, or a stick, &c., would attract them; but care would be required in making the experiment, from the readiness with which these threads would move upon disturbance of the air. If electric, then it would be important to know whether they were positive or negative; which their attraction, or repulsion, by a stick of sealing-wax, rubbed on the sleeve of a coat, would at once determine. It is well known that these threads are almost perfect insulators of electricity, and would retain a charged state for a long time in a dry sunny atmosphere.—Brande's Journal.
The following directions, by M. Douette Richardot, are to enable the amateur to gather as fine roses in September as he did in the preceding June:—1. Immediately after the first flowering, the shrub is to be deprived of every leaf, and those branches which have borne roses cut so that only two or three buds shall remain. The cutting of the weaker branches may be in a less degree. If the weather be dry when the leaves are removed, it will be necessary to thoroughly water the stem, for several days, with the rose of the watering-pot: in this way the sap will not be arrested. 2. Then the brush is to be used, and the rose tree well cleansed by it, so that all mouldiness shall disappear: this operation is very easy after an abundant rain. 3. The earth about the rose tree is to be disturbed, and then twenty-four sockets of calves' feet are to be placed in the earth round the stem, and about four inches distant from it. The hoofs of young calves are the best, and give a vivid colour and agreeable perfume to the roses. These are to be placed with the points downwards, so that the cups shall be nearly level with the surface of the earth, and the plant well surrounded. This operation is to be repeated in the November following. These hoofs, dissolved by the rain or the waterings, form an excellent manure, which hastens the vegetation, and determines the reproduction of flowers. 4. Two waterings per week will suffice in ordinary weather, and they should be made with the rose of the watering-pot, so that the hoofs may be filled; but, if the atmosphere is dry, it will be necessary to water the plants every evening; and in the latter case it will be necessary, from time to time, to direct the stream of water on to the head of the tree.—From the French.
Mr. Samuel Mitchell has, in his "Summary of the Progress of Natural Science for the last few Years," given an amusing account of the progress of sea-serpentism. It was read before the New York Lyceum, and is inserted in the American Journal of Science, although not thought conclusive by its learned editor, Dr. Silliman. The first sea-serpent was a steam-boat, which, being established at Boston to coast along the shore, and from its powers and capabilities competent to injure the business of small boats, was described as a sea-serpent that had been seen off Nahant and Gloucester, and had probably come there to consume all the small fish in the place. This was received by many as a serious account, and believed accordingly.
Another sea-serpent history arose from the circumstance, that a small sloop, called the Sea-Serpent, having been passed by another vessel, the captain of the latter, when asked, upon his arrival at home, for news, said he had seen a sea-serpent, and then described its bunches on the back, [pg 256] the action of its tail, and other parts; all of which being understood literally, actually appeared in print, as evidence for the existence of the animal.
Then a piece of the skin of the bony scaled pike was taken for part of a sea-serpent's hide. A speckled mother duck, with a numerous brood of young ones swimming after her in a line on Lake Ontario, was described as the sea-serpent itself. And from such occurrences as these, perhaps, mingled with careless observation of the motions and appearances of porpuses, basking sharks, and balænopterous whales, appears to have originated every thing that has been said about American sea-serpents.—Brande's Jour.
A snapper up of unconsidered trifles.
SHAKSPEARE.
A French officer, having arrived at the court of Vienna, the empress, knowing that he had seen the Princess de * * *, asked him if he thought this princess was, as reported, the handsomest person in the world? "Madam," replied the officer, "I thought so yesterday."
Should women sit in parliament,
A thing unprecedented,
A great part of the nation, then
Would be Miss-Represented.
This wall was made at ye charges of ye Right Honorable and trulie pious Lorde Francis Russell, Earle of Bedford, out of true zeale and care for ye keeping of this church-yard, and ye wardrobe of Godd's saints, whose bodies lay theirin buried from violation by swine, and other prophanation.—So witnesseth William Walker, Vo. A.D. 1623.
O.W.
A singular custom was formerly observed in the city of Middelburg, in the Netherlands. When any inhabitant died, a bundle of straw was placed before the house, with the ears towards the street, if the deceased was a man; but towards the house, if a woman.
G.W.N.
In 1767, a gentleman, named Davers, (who was descended from Sir Robert Davers, of Roughham, in the county of Suffolk, bart.) died at the Angel Inn, Islington, by poison. A card, which he was seen to write a few hours before his death, contained the following words:—"Descended from an ancient and honourable family, I have, for fifteen years past, suffered more indigence than ever gentleman before submitted to. I am neglected by my acquaintance, traduced by my enemies, and insulted by the vulgar." Beneath the above was written:—
"Of laudanum, an ample dose
Must all my present ills compose;
But the best of laudanum all,
I want; not resolution, but a ball."
G.W.N.
It is well known that the Turks avoid answering questions put to them concerning their religion, to prevent being exposed to criticism and raillery. A lady of quality reproached a Turkish ambassador, on the Mahometan religion allowing them to have several wives. The ambassador, without entering into any discussion, replied, "It permits it, that we may be able to find in several, all the graces which are concentrated in you alone."
John Daens, merchant and citizen of Antwerp, having lent the Emperor Charles V. a million of gold, invited his majesty to dinner. After a royal entertainment, he threw the emperor's bond into a fire made of cinnamon.
G.W.N.
Purchasers of the MIRROR, who may wish to complete their sets are informed, that every volume is complete in itself, and may be purchased separately. The whole of the numbers are now in print, and can be procured by giving an order to any Bookseller or Newsvender.
Complete sets Vol I. to XII. in boards, price £3. 5s. half bound, £4. 2s. 6d.
CHEAP and POPULAR WORKS published at the MIRROR OFFICE in the Strand, near Somerset House.
The ARABIAN NIGHTS' ENTERTAINMENTS. Embellished with nearly 150 Engravings. Price 6s. 6d. boards.
The TALES of the GENII. Price 2s.
The MICROCOSM By the Right Hon. G. CANNING. &c. Price 2s.
PLUTARCH'S LIVES, with Fifty Portraits, 2 vols. price 13s. boards.
COWPER'S POEMS, with 12 Engravings, price 3s. 6d. boards.
COOK'S VOYAGES, 2 vols. price 8s. boards.
The CABINET of CURIOSITIES: or WONDERS of the WORLD DISPLAYED Price 5s. boards.
BEAUTIES of SCOTT, 2 vols. price 7s. boards.
The ARCANA of SCIENCE for 1828. Price 4s. 6d.
Any of the above Works can be purchased in Parts.
GOLDSMITH'S ESSAYS. Price 8d.
DR. FRANKLIN'S ESSAYS. Price 4s. 2d.
BACON'S ESSAYS Price 8d.
SALMAGUNDI. Price 1s. 8d.
Printed and Published by J. LIMBIRD 143, Strand. (near Somerset House,) London; sold by ERNEST FLEISCHER, 626, New Market', Leipsic; and by all Newsmen and Booksellers.
Footnote 1:(return)The present Strand Lane (as it would seem to have been called in Strype's time) skirts the eastern side of Somerset House, and forms a boundary between the parishes of St. Mary and St. Clement Danes. At its stairs, which are still, as formerly, "a place of some note to take water at," is the outlet of a small underground stream.
Footnote 2:(return)Inigo Jones died at Somerset House, July 21, 1651.
Footnote 3:(return)Or Wittenagemote, i.e. assembly of wise men.
Footnote 4:(return)Of this house, we have given an accurate Engraving at page 8 in the present volume.
Footnote 5:(return)Mr. Jonathan Stubbs retired from business long before he reached his grand climacteric, to his country house at Newington Butts, with the solid dignity of at least half a plum. What length of years might have been in store for him, if he had regularly taken Dr. James's analeptic pills, it is impossible to say; but not doing so, he had occasion to send the coachman one night for an ounce of Epsom salts. They proved to be oxalic acid; and stomach-pumps not being then in existence, there was an inevitable termination to the existence of Mr. Stubbs. An "extraordinary sensation," as the newspapers have it, was produced in Newington Butts by this dreadful catastrophe.
Printed and Published by J. LIMBIRD 143, Strand. (near Somerset House,) London; sold by ERNEST FLEISCHER, 626, New Market, Leipsic; and by all Newsmen and Booksellers.
End of the Project Gutenberg EBook of The Mirror of Literature, Amusement,
and Instruction, No. 365, by Various
*** END OF THIS PROJECT GUTENBERG EBOOK MIRROR OF LITERATURE ***
***** This file should be named 3246-h.htm or 3246-h.zip *****
This and all associated files of various formats will be found in:
http://www.gutenberg.net/3/2/4/3246/
Produced by Jonathan Ingram and PG Distributed Proofreaders
Updated editions will replace the previous one--the old editions
will be renamed.
Creating the works from public domain print editions means that no
one owns a United States copyright in these works, so the Foundation
(and you!) can copy and distribute it in the United States without
permission and without paying copyright royalties. Special rules,
set forth in the General Terms of Use part of this license, apply to
copying and distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works to
protect the PROJECT GUTENBERG-tm concept and trademark. Project
Gutenberg is a registered trademark, and may not be used if you
charge for the eBooks, unless you receive specific permission. If you
do not charge anything for copies of this eBook, complying with the
rules is very easy. You may use this eBook for nearly any purpose
such as creation of derivative works, reports, performances and
research. They may be modified and printed and given away--you may do
practically ANYTHING with public domain eBooks. Redistribution is
subject to the trademark license, especially commercial
redistribution.
*** START: FULL LICENSE ***
THE FULL PROJECT GUTENBERG LICENSE
PLEASE READ THIS BEFORE YOU DISTRIBUTE OR USE THIS WORK
To protect the Project Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting the free
distribution of electronic works, by using or distributing this work
(or any other work associated in any way with the phrase "Project
Gutenberg"), you agree to comply with all the terms of the Full Project
Gutenberg-tm License (available with this file or online at
http://gutenberg.net/license).
Section 1. General Terms of Use and Redistributing Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic works
1.A. By reading or using any part of this Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work, you indicate that you have read, understand, agree to
and accept all the terms of this license and intellectual property
(trademark/copyright) agreement. If you do not agree to abide by all
the terms of this agreement, you must cease using and return or destroy
all copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in your possession.
If you paid a fee for obtaining a copy of or access to a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work and you do not agree to be bound by the
terms of this agreement, you may obtain a refund from the person or
entity to whom you paid the fee as set forth in paragraph 1.E.8.
1.B. "Project Gutenberg" is a registered trademark. It may only be
used on or associated in any way with an electronic work by people who
agree to be bound by the terms of this agreement. There are a few
things that you can do with most Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works
even without complying with the full terms of this agreement. See
paragraph 1.C below. There are a lot of things you can do with Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works if you follow the terms of this agreement
and help preserve free future access to Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works. See paragraph 1.E below.
1.C. The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation ("the Foundation"
or PGLAF), owns a compilation copyright in the collection of Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic works. Nearly all the individual works in the
collection are in the public domain in the United States. If an
individual work is in the public domain in the United States and you are
located in the United States, we do not claim a right to prevent you from
copying, distributing, performing, displaying or creating derivative
works based on the work as long as all references to Project Gutenberg
are removed. Of course, we hope that you will support the Project
Gutenberg-tm mission of promoting free access to electronic works by
freely sharing Project Gutenberg-tm works in compliance with the terms of
this agreement for keeping the Project Gutenberg-tm name associated with
the work. You can easily comply with the terms of this agreement by
keeping this work in the same format with its attached full Project
Gutenberg-tm License when you share it without charge with others.
1.D. The copyright laws of the place where you are located also govern
what you can do with this work. Copyright laws in most countries are in
a constant state of change. If you are outside the United States, check
the laws of your country in addition to the terms of this agreement
before downloading, copying, displaying, performing, distributing or
creating derivative works based on this work or any other Project
Gutenberg-tm work. The Foundation makes no representations concerning
the copyright status of any work in any country outside the United
States.
1.E. Unless you have removed all references to Project Gutenberg:
1.E.1. The following sentence, with active links to, or other immediate
access to, the full Project Gutenberg-tm License must appear prominently
whenever any copy of a Project Gutenberg-tm work (any work on which the
phrase "Project Gutenberg" appears, or with which the phrase "Project
Gutenberg" is associated) is accessed, displayed, performed, viewed,
copied or distributed:
This eBook is for the use of anyone anywhere at no cost and with
almost no restrictions whatsoever. You may copy it, give it away or
re-use it under the terms of the Project Gutenberg License included
with this eBook or online at www.gutenberg.net
1.E.2. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is derived
from the public domain (does not contain a notice indicating that it is
posted with permission of the copyright holder), the work can be copied
and distributed to anyone in the United States without paying any fees
or charges. If you are redistributing or providing access to a work
with the phrase "Project Gutenberg" associated with or appearing on the
work, you must comply either with the requirements of paragraphs 1.E.1
through 1.E.7 or obtain permission for the use of the work and the
Project Gutenberg-tm trademark as set forth in paragraphs 1.E.8 or
1.E.9.
1.E.3. If an individual Project Gutenberg-tm electronic work is posted
with the permission of the copyright holder, your use and distribution
must comply with both paragraphs 1.E.1 through 1.E.7 and any additional
terms imposed by the copyright holder. Additional terms will be linked
to the Project Gutenberg-tm License for all works posted with the
permission of the copyright holder found at the beginning of this work.
1.E.4. Do not unlink or detach or remove the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License terms from this work, or any files containing a part of this
work or any other work associated with Project Gutenberg-tm.
1.E.5. Do not copy, display, perform, distribute or redistribute this
electronic work, or any part of this electronic work, without
prominently displaying the sentence set forth in paragraph 1.E.1 with
active links or immediate access to the full terms of the Project
Gutenberg-tm License.
1.E.6. You may convert to and distribute this work in any binary,
compressed, marked up, nonproprietary or proprietary form, including any
word processing or hypertext form. However, if you provide access to or
distribute copies of a Project Gutenberg-tm work in a format other than
"Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other format used in the official version
posted on the official Project Gutenberg-tm web site (www.gutenberg.net),
you must, at no additional cost, fee or expense to the user, provide a
copy, a means of exporting a copy, or a means of obtaining a copy upon
request, of the work in its original "Plain Vanilla ASCII" or other
form. Any alternate format must include the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License as specified in paragraph 1.E.1.
1.E.7. Do not charge a fee for access to, viewing, displaying,
performing, copying or distributing any Project Gutenberg-tm works
unless you comply with paragraph 1.E.8 or 1.E.9.
1.E.8. You may charge a reasonable fee for copies of or providing
access to or distributing Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works provided
that
- You pay a royalty fee of 20% of the gross profits you derive from
the use of Project Gutenberg-tm works calculated using the method
you already use to calculate your applicable taxes. The fee is
owed to the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark, but he
has agreed to donate royalties under this paragraph to the
Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation. Royalty payments
must be paid within 60 days following each date on which you
prepare (or are legally required to prepare) your periodic tax
returns. Royalty payments should be clearly marked as such and
sent to the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation at the
address specified in Section 4, "Information about donations to
the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation."
- You provide a full refund of any money paid by a user who notifies
you in writing (or by e-mail) within 30 days of receipt that s/he
does not agree to the terms of the full Project Gutenberg-tm
License. You must require such a user to return or
destroy all copies of the works possessed in a physical medium
and discontinue all use of and all access to other copies of
Project Gutenberg-tm works.
- You provide, in accordance with paragraph 1.F.3, a full refund of any
money paid for a work or a replacement copy, if a defect in the
electronic work is discovered and reported to you within 90 days
of receipt of the work.
- You comply with all other terms of this agreement for free
distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm works.
1.E.9. If you wish to charge a fee or distribute a Project Gutenberg-tm
electronic work or group of works on different terms than are set
forth in this agreement, you must obtain permission in writing from
both the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation and Michael
Hart, the owner of the Project Gutenberg-tm trademark. Contact the
Foundation as set forth in Section 3 below.
1.F.
1.F.1. Project Gutenberg volunteers and employees expend considerable
effort to identify, do copyright research on, transcribe and proofread
public domain works in creating the Project Gutenberg-tm
collection. Despite these efforts, Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works, and the medium on which they may be stored, may contain
"Defects," such as, but not limited to, incomplete, inaccurate or
corrupt data, transcription errors, a copyright or other intellectual
property infringement, a defective or damaged disk or other medium, a
computer virus, or computer codes that damage or cannot be read by
your equipment.
1.F.2. LIMITED WARRANTY, DISCLAIMER OF DAMAGES - Except for the "Right
of Replacement or Refund" described in paragraph 1.F.3, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation, the owner of the Project
Gutenberg-tm trademark, and any other party distributing a Project
Gutenberg-tm electronic work under this agreement, disclaim all
liability to you for damages, costs and expenses, including legal
fees. YOU AGREE THAT YOU HAVE NO REMEDIES FOR NEGLIGENCE, STRICT
LIABILITY, BREACH OF WARRANTY OR BREACH OF CONTRACT EXCEPT THOSE
PROVIDED IN PARAGRAPH F3. YOU AGREE THAT THE FOUNDATION, THE
TRADEMARK OWNER, AND ANY DISTRIBUTOR UNDER THIS AGREEMENT WILL NOT BE
LIABLE TO YOU FOR ACTUAL, DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, PUNITIVE OR
INCIDENTAL DAMAGES EVEN IF YOU GIVE NOTICE OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGE.
1.F.3. LIMITED RIGHT OF REPLACEMENT OR REFUND - If you discover a
defect in this electronic work within 90 days of receiving it, you can
receive a refund of the money (if any) you paid for it by sending a
written explanation to the person you received the work from. If you
received the work on a physical medium, you must return the medium with
your written explanation. The person or entity that provided you with
the defective work may elect to provide a replacement copy in lieu of a
refund. If you received the work electronically, the person or entity
providing it to you may choose to give you a second opportunity to
receive the work electronically in lieu of a refund. If the second copy
is also defective, you may demand a refund in writing without further
opportunities to fix the problem.
1.F.4. Except for the limited right of replacement or refund set forth
in paragraph 1.F.3, this work is provided to you 'AS-IS' WITH NO OTHER
WARRANTIES OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTIBILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PURPOSE.
1.F.5. Some states do not allow disclaimers of certain implied
warranties or the exclusion or limitation of certain types of damages.
If any disclaimer or limitation set forth in this agreement violates the
law of the state applicable to this agreement, the agreement shall be
interpreted to make the maximum disclaimer or limitation permitted by
the applicable state law. The invalidity or unenforceability of any
provision of this agreement shall not void the remaining provisions.
1.F.6. INDEMNITY - You agree to indemnify and hold the Foundation, the
trademark owner, any agent or employee of the Foundation, anyone
providing copies of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works in accordance
with this agreement, and any volunteers associated with the production,
promotion and distribution of Project Gutenberg-tm electronic works,
harmless from all liability, costs and expenses, including legal fees,
that arise directly or indirectly from any of the following which you do
or cause to occur: (a) distribution of this or any Project Gutenberg-tm
work, (b) alteration, modification, or additions or deletions to any
Project Gutenberg-tm work, and (c) any Defect you cause.
Section 2. Information about the Mission of Project Gutenberg-tm
Project Gutenberg-tm is synonymous with the free distribution of
electronic works in formats readable by the widest variety of computers
including obsolete, old, middle-aged and new computers. It exists
because of the efforts of hundreds of volunteers and donations from
people in all walks of life.
Volunteers and financial support to provide volunteers with the
assistance they need, is critical to reaching Project Gutenberg-tm's
goals and ensuring that the Project Gutenberg-tm collection will
remain freely available for generations to come. In 2001, the Project
Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation was created to provide a secure
and permanent future for Project Gutenberg-tm and future generations.
To learn more about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation
and how your efforts and donations can help, see Sections 3 and 4
and the Foundation web page at http://www.pglaf.org.
Section 3. Information about the Project Gutenberg Literary Archive
Foundation
The Project Gutenberg Literary Archive Foundation is a non profit
501(c)(3) educational corporation organized under the laws of the
state of Mississippi and granted tax exempt status by the Internal
Revenue Service. The Foundation's EIN or federal tax identification
number is 64-6221541. Its 501(c)(3) letter is posted at
http://pglaf.org/fundraising. Contributions to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation are tax deductible to the full extent
permitted by U.S. federal laws and your state's laws.
The Foundation's principal office is located at 4557 Melan Dr. S.
Fairbanks, AK, 99712., but its volunteers and employees are scattered
throughout numerous locations. Its business office is located at
809 North 1500 West, Salt Lake City, UT 84116, (801) 596-1887, email
business@pglaf.org. Email contact links and up to date contact
information can be found at the Foundation's web site and official
page at http://pglaf.org
For additional contact information:
Dr. Gregory B. Newby
Chief Executive and Director
gbnewby@pglaf.org
Section 4. Information about Donations to the Project Gutenberg
Literary Archive Foundation
Project Gutenberg-tm depends upon and cannot survive without wide
spread public support and donations to carry out its mission of
increasing the number of public domain and licensed works that can be
freely distributed in machine readable form accessible by the widest
array of equipment including outdated equipment. Many small donations
($1 to $5,000) are particularly important to maintaining tax exempt
status with the IRS.
The Foundation is committed to complying with the laws regulating
charities and charitable donations in all 50 states of the United
States. Compliance requirements are not uniform and it takes a
considerable effort, much paperwork and many fees to meet and keep up
with these requirements. We do not solicit donations in locations
where we have not received written confirmation of compliance. To
SEND DONATIONS or determine the status of compliance for any
particular state visit http://pglaf.org
While we cannot and do not solicit contributions from states where we
have not met the solicitation requirements, we know of no prohibition
against accepting unsolicited donations from donors in such states who
approach us with offers to donate.
International donations are gratefully accepted, but we cannot make
any statements concerning tax treatment of donations received from
outside the United States. U.S. laws alone swamp our small staff.
Please check the Project Gutenberg Web pages for current donation
methods and addresses. Donations are accepted in a number of other
ways including including checks, online payments and credit card
donations. To donate, please visit: http://pglaf.org/donate
Section 5. General Information About Project Gutenberg-tm electronic
works.
Professor Michael S. Hart is the originator of the Project Gutenberg-tm
concept of a library of electronic works that could be freely shared
with anyone. For thirty years, he produced and distributed Project
Gutenberg-tm eBooks with only a loose network of volunteer support.
Project Gutenberg-tm eBooks are often created from several printed
editions, all of which are confirmed as Public Domain in the U.S.
unless a copyright notice is included. Thus, we do not necessarily
keep eBooks in compliance with any particular paper edition.
Most people start at our Web site which has the main PG search facility:
http://www.gutenberg.net
This Web site includes information about Project Gutenberg-tm,
including how to make donations to the Project Gutenberg Literary
Archive Foundation, how to help produce our new eBooks, and how to
subscribe to our email newsletter to hear about new eBooks.